Degenerative Disc Disease
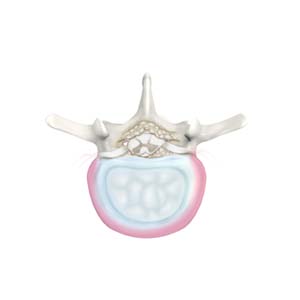
DISC ANATOMY
The intervertebral disc is composed of an inflexible ring called the annulus fibrosis which encloses a gelatinous inner structure called the nucleus pulposus. The intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers.
WHAT IS DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE?
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) refers to gradual deterioration of the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae. DDD is a misnomer as it is not actually a disease but a condition that affects the strength, resiliency and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to advancing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture, or poor body mechanics. DDD is present in all individuals over 50 years of age and usually develops sooner Most degenerative discs are completely painless.
CAUSES OF DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE
As we age, the rate at which the old, worn out cells are replaced is gradually reduced, resulting in the degenerative changes in the discs which can also be accelerated by injury or trauma.
These structural changes can cause a sequence of other changes, resulting in nerve compression and pain due to reduction in the disc height, and presence of bone spurs or bony overgrowths (osteophytes).
SYMPTOMS OF DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE
Every patient is different, and it is important to realize that not everyone develops symptoms because of degenerative disc disease. When the condition becomes symptomatic, it can manifest in different ways. Depending on the location of the degenerative disc, it could cause back pain, radiating leg pain, neck pain, and radiating arm pain.
DIAGNOSIS OF DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE
Examination of the back for flexibility, range of motion, and the presence of certain signs that suggest nerve root injury help detect the degenerative changes. This is done by testing your muscle strength and your reflexes to make sure that they are still functioning normally. Imaging including X-rays and sometimes CT or MRI may be needed as well.
TREATMENT OF DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE
Both surgical and non-surgical treatment options are available for the management of degenerative conditions. The choice of treatment depends on various factors such as age of patient and severity of the disease.
Nonsurgical treatment is almost always preferred rather than operative care unless the symptoms fail to respond. Nonsurgical treatment can consist of exercise, activity modification, bracing, physical therapy, medication, injections and other pain management modalities.
Related Links
- Neck Pain
- Whiplash
- Back Pain
- Lumbar Radiculopathy
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Disc Herniation
- Facet joint Arthritis
- Sciatica
- Spondylolysis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Vertebral Compression Fractures
- Scoliosis
- Kyphosis
- Cervical Disc Herniation
- Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Cervical Radiculopathy/Myelopathy
- Cervical Stenosis
- Lumbar Stenosis
